Self learning AI refers to intelligent systems that can identify patterns, learn behaviors, and improve decision-making by analyzing data instead of relying entirely on fixed, rule-based programming.
Unlike traditional software that behaves exactly as it is coded, self learning AI evolves through experience. As more data is processed, performance improves naturally, making the system more accurate, efficient, and adaptable over time.
Key characteristics include:
- Continuous improvement through incoming data
- Ability to adapt to changing environments
- Reduced reliance on manual updates
- Long-term performance enhancement
These traits make modern intelligent systems scalable and suitable for real-world complexity.
Table of Contents
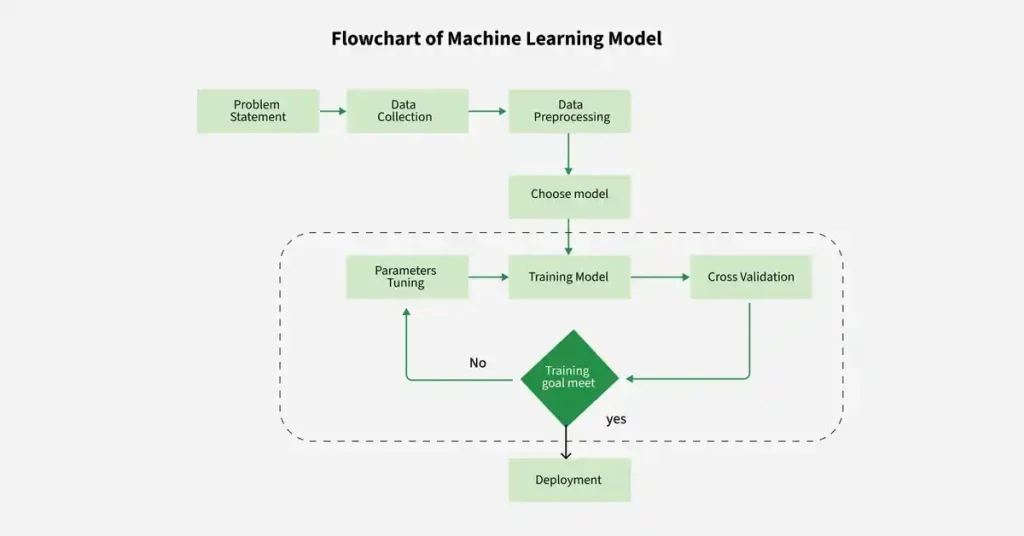
How Self Learning AI Works (Step-by-Step)
At its core, self learning AI follows a structured learning loop. While technical implementations may vary, the fundamental process remains consistent.
1. Data Collection
The system gathers information from user interactions, sensors, logs, transactions, or external datasets. Learning accuracy depends heavily on data quality and diversity.
2. Pattern Recognition
Using mathematical models and neural networks, the system identifies trends, correlations, and anomalies within the collected data.
3. Model Training
Based on discovered patterns, internal models are refined to improve predictions and decision-making. Training can happen continuously or at scheduled intervals.
4. Feedback and Evaluation
Performance is evaluated through predefined metrics. In many intelligent systems, feedback is generated automatically from real-world usage.
5. Optimization
Parameters are adjusted to reduce errors and enhance future outcomes.
This loop repeats, allowing self learning AI to evolve without constant human intervention.
Types of Learning Models Used in AI Systems
Different learning approaches are applied depending on the problem being solved. Understanding these models clarifies how adaptive systems function.
Supervised Learning
The system learns from labeled datasets curated by humans.
Example: Email spam classification.
Unsupervised Learning
Patterns are discovered without labeled data, making it ideal for exploratory analysis.
Example: Customer behavior segmentation.
Reinforcement Learning
The system learns through trial and error by receiving rewards or penalties.
Example: Game-playing agents or robotic navigation.
Deep Learning
This approach uses multi-layer neural networks to handle complex tasks such as vision and language processing.
Most advanced self learning AI implementations rely on deep learning architectures.
Real-World Applications
Today, self learning AI is embedded across industries, often operating quietly in the background.
Healthcare
Medical data is analyzed to assist diagnostics, predict disease risks, and recommend treatments. Each new case improves system accuracy.
Finance
Banks and fintech platforms detect evolving fraud patterns by continuously learning from transaction behavior.
E-commerce and Content Platforms
Recommendation engines refine product and content suggestions by learning from user interactions.
Autonomous Vehicles
Driving systems adapt to traffic conditions, weather, and road environments using real-time feedback.
Cybersecurity
Network activity is monitored to identify emerging threats without depending solely on static rules.
Why Self Learning AI Is So Powerful
The real strength of self learning AI lies in its adaptability.
Key Advantages
- Scalability: Performance improves as data grows
- Efficiency: Reduced need for manual system updates
- Accuracy: Continuous learning minimizes errors
- Resilience: Ability to respond to new and unseen patterns
Unlike static automation, learning-based systems remain relevant even as environments change.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its benefits, self learning AI introduces notable challenges that require careful management.
Data Bias
If training data contains bias, the system may reinforce unfair or inaccurate outcomes.
Lack of Transparency
Complex models can behave like “black boxes,” making decisions difficult to explain.
Overfitting
Learning too narrowly from specific datasets can reduce general usability.
Security Threats
Malicious data inputs may manipulate system behavior if safeguards are weak.
Responsible deployment requires governance, monitoring, and ethical oversight.
Comparison With Traditional Automation
| Feature | Traditional Software | Learning-Based Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptability | None | Continuous |
| Data Utilization | Limited | Extensive |
| Manual Updates | Frequent | Minimal |
| Long-Term Performance | Static | Improves |
This contrast explains why many organizations are shifting toward adaptive intelligence.
The Future of Self Learning AI
The next phase of development will emphasize autonomy combined with responsibility.
Self learning AI will increasingly operate with built-in safety, transparency, and ethical constraints.
Expected trends include:
- Greater independent decision-making
- Cross-domain learning capabilities
- Reduced dependence on massive real-world datasets
As regulation improves, self learning AI adoption will accelerate.
How Businesses Can Prepare
Organizations planning to adopt self learning AI should focus on:
- High-quality, unbiased data pipelines
- Continuous performance monitoring
- Clear accountability frameworks
- Human oversight for critical decisions
Successful adoption is not only technical—it is strategic.
Final Thoughts
Self learning AI represents a fundamental shift in how technology evolves. Instead of relying on static instructions, systems now learn from experience, adapt to change, and improve continuously.
Across healthcare, finance, security, and automation, self learning AI is becoming core infrastructure. Understanding how it works—and how to use it responsibly—is now essential.
As data ecosystems expand and models mature, intelligent learning systems will shape the next era of digital transformation.
