AI machine learning is no longer a theoretical concept discussed only in research labs or tech conferences. It has become an operational layer of modern digital systems, influencing how platforms analyze data, automate decisions, and adapt to user behavior. Whether users are aware of it or not, learning-based systems now play a role in shaping everyday digital experiences.
At its core, ai machine learning focuses on enabling systems to improve performance through data rather than relying entirely on fixed instructions. This shift has changed how software is designed, maintained, and scaled. Instead of manually adjusting logic for every scenario, developers train models that learn patterns from real-world inputs.
Understanding this technology does not require a technical background. What matters more is knowing what these systems can realistically do, where they are effective, and where limitations still exist.
Table of Contents
What AI and Machine Learning Actually Mean
The term artificial intelligence often creates unrealistic expectations. In practice, ai machine learning systems are not thinking entities. They are tools designed to identify patterns, make predictions, and support decision-making within defined boundaries.
Artificial intelligence refers to the broader objective of simulating intelligent behavior, while machine learning is the method used to achieve that objective. When combined effectively, they allow systems to improve accuracy and efficiency over time.
How Machine Learning Systems Learn From Data
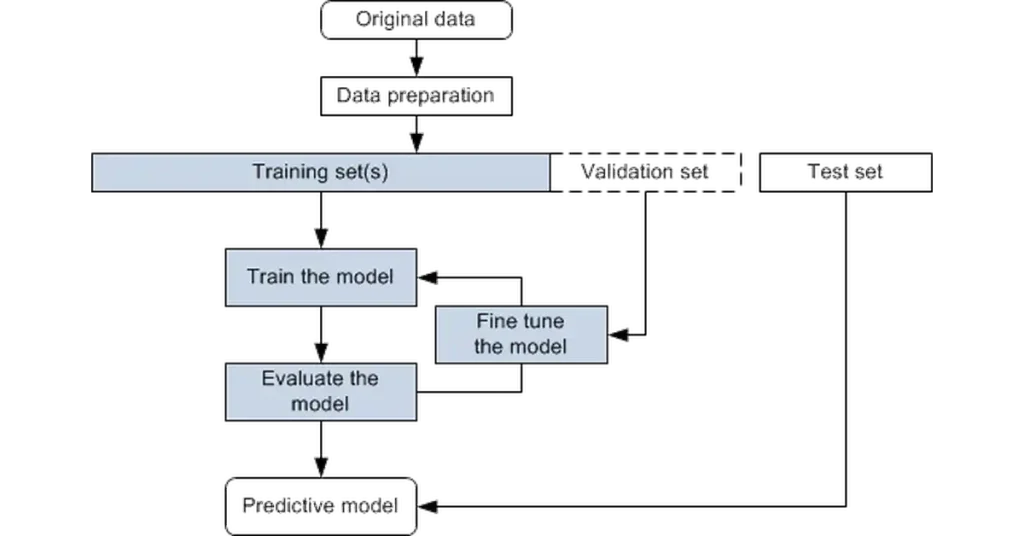
A typical learning system follows a structured process:
- Data collection from real-world sources
- Data cleaning and preparation
- Model training using historical examples
- Testing and validation
- Deployment into live systems
- Ongoing monitoring and updates
This cycle allows ai machine learning models to adapt as new data becomes available, making them more useful in dynamic environments.
Key Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
Different problems require different learning approaches. Common categories include:
Supervised Learning
Used when outcomes are known in advance, such as classification and prediction tasks.
Unsupervised Learning
Used to discover hidden patterns or groupings in data without predefined labels.
Reinforcement Learning
Used in environments where decisions lead to feedback and rewards over time.
These machine learning algorithms are selected based on the nature of the problem, data availability, and required accuracy.
Where AI Machine Learning Is Used Today
Real-world applications are already widespread. AI machine learning is commonly used in:
- Search ranking and recommendation systems
- Fraud and anomaly detection
- Automated moderation tools
- Voice and image recognition
- Predictive analytics
These systems are valued not because they replace humans, but because they operate efficiently at scale.
Strengths and Practical Benefits
When implemented correctly, ai machine learning offers several advantages:
- High-speed data processing
- Consistent decision-making
- Scalability across large systems
- Continuous performance improvement
These strengths explain why adoption continues to grow across industries.
Limitations and Realistic Expectations
Despite its benefits, ai machine learning has clear limitations. Models depend heavily on data quality and can inherit biases present in training datasets. They also struggle with scenarios outside their learned patterns.
Understanding these limits is essential for responsible use and realistic expectations.
Ethics, Trust, and Responsible Use
As reliance increases, organizations must address transparency, fairness, and accountability. Responsible deployment of ai machine learning requires clear governance, human oversight, and ongoing evaluation.
This is especially important in regions with strong data protection and regulatory standards.
What the Future Likely Holds
Rather than moving toward fully autonomous intelligence, the future of ai machine learning points toward specialized, task-focused systems that are easier to control and explain. Efficiency, reliability, and trust will matter more than novelty.
Conclusion
AI machine learning is best understood as a practical tool rather than a mysterious force. It already shapes how digital systems operate and will continue to influence technology development in measurable ways. By understanding how it works, its strengths, and its limitations, users and decision-makers can engage with it more confidently and responsibly.
